
Strategic efforts in inflation management, interest rate stabilization, and infrastructure investment formed the backbone of the country’s economic resilience
Kampala, Uganda | JULIUS BUSINGE | Uganda’s economic performance in 2024 highlighted its ability to navigate global and domestic challenges while leveraging opportunities to bolster growth. Strategic efforts in inflation management, interest rate stabilization, and infrastructure investment formed the backbone of the country’s economic resilience. These measures underscored Uganda’s commitment to sustaining momentum in an evolving economic landscape.
Key sectors, including agriculture, services, and mining, were instrumental in driving this progress, offering a roadmap for future policy and strategic investments. As the country positions itself for sustained growth, its achievements in 2024 offer valuable lessons and direction for navigating modern economic complexities.
Inflation management
Inflation stood as a defining theme in Uganda’s economic narrative in 2024. Despite external shocks and domestic pressures, inflation rates were successfully contained, remaining below the Bank of
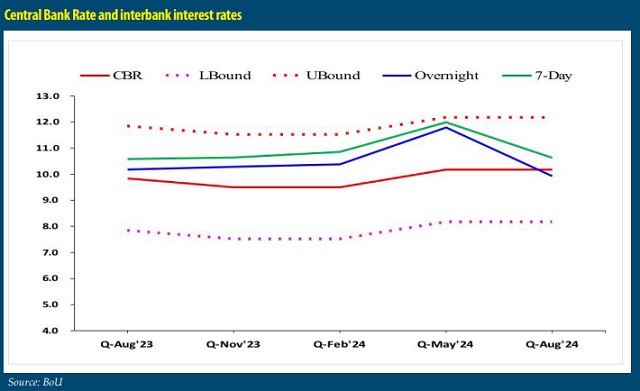
Uganda’s medium-term target of 5%. The Central Bank adopted a proactive stance, raising the Central Bank Rate (CBR) to 10% by mid-year to curb inflationary pressures. This tight monetary policy approach demonstrated a fine balance between curbing inflation and fostering economic growth.
Key contributors to inflation stabilization included improved agricultural output, particularly in staple crops like maize, coffee, and bananas. Enhanced productivity helped mitigate food price volatility, while adjustments in the energy sector addressed supply chain disruptions. Additionally, global oil prices showed moderation, providing relief from external inflationary pressures.
GDP growth and sectoral performance
Uganda’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) grew by an estimated 5.2% in 2024, exceeding initial projections of 4.8%. This growth reflected the government’s focus on strategic investments and policy alignment. The National Budget for FY 2023/24 anticipated a 6% growth rate, with projections for FY 2024/25 rising to 6.4%.
Agriculture, which contributed approximately 26% of GDP, experienced robust growth of 6.5%. Favorable weather conditions and improved market access boosted yields of staple crops, supporting rural incomes and food security. The services sector, accounting for 50% of GDP, recorded significant expansion driven by tourism, telecommunications, and financial services. Tourism grew by 10% due to increased international arrivals and improved infrastructure, while mobile money transactions surged to Shs70 trillion ($19 billion), reflecting deeper digitization of financial services.
Mining and manufacturing also played pivotal roles. Mining output rose by 7%, fueled by demand for gold, lithium, and cobalt, aligning with global trends in critical minerals. The manufacturing sector grew by 5.5%, supported by government initiatives promoting industrialization and local content development. These advancements positioned Uganda strategically within regional and global value chains.
Budgetary allocations and fiscal policy
The national budget for FY 2024/25 increased by 36% to Shs72.1 trillion, underscoring the government’s emphasis on infrastructure development. Energy, transportation, and ICT accounted for 30% of total expenditures. Major projects like the East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP) and hydropower initiatives at Karuma and Isimba absorbed significant resources, signaling the government’s commitment to leveraging oil and energy potential.
Social sectors also saw increased funding. Health sector initiatives prioritized disease prevention and expanded healthcare access, while education programs focused on improving quality and accessibility in primary and secondary schools. These investments highlighted the government’s focus on human capital development as a driver of long-term economic growth.
Exchange rate and interest rate dynamics
The Ugandan shilling demonstrated relative stability against the US dollar throughout 2024, with appreciation trends emerging by March. Increased export revenues, particularly from coffee, supported the currency’s performance. However, depreciation pressures surfaced in the latter half of the year due to heightened dollar demand from key sectors such as manufacturing and telecoms. By August, the shilling had stabilized, supported by inflows from NGOs, coffee exports, and offshore investments.
Interest rates reflected the Central Bank’s monetary policy stance, with average prime lending rates climbing to 17% by yearend from 15% at the start of 2024. While higher rates posed challenges for credit access, they effectively anchored inflation expectations. The Uganda Development Bank (UDB) played a critical role in extending concessional loans to sectors like agriculture, energy, and manufacturing, spurring private sector activity.
Structural advancements and growth drivers
Critical sectors drove Uganda’s economic growth in 2024. Agriculture’s resilience was supported by improved weather patterns and targeted government interventions. Services sectors, particularly tourism and telecommunications, demonstrated innovation and adaptability, contributing significantly to GDP growth. Mining and manufacturing capitalized on global trends, while energy and infrastructure investments alleviated longstanding bottlenecks.
The energy sector’s advancements, including the addition of 600 MW from the Karuma hydropower plant, reduced power shortages and lowered business costs. These developments underscored the symbiotic relationship between infrastructure investments and economic growth.
Challenges and opportunities ahead
Despite notable achievements, challenges persisted. Inflationary pressures, volatile global commodity prices, and infrastructure gaps in remote areas posed risks to sustained growth. Addressing skills deficits in key sectors such as mining and manufacturing will be crucial for inclusivity and long-term progress.
Looking ahead to 2025, Uganda’s economic outlook remains optimistic. Continued investments in agriculture, energy, and critical minerals are expected to drive growth. Regional cooperation frameworks like the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) and the African Mining Vision will further enhance competitiveness and global market integration.
In a nutshell, Uganda’s economic performance in 2024 exemplified resilience and strategic foresight. With inflation contained, GDP growth exceeding expectations, and critical investments paving the way for future development, the country demonstrated its capacity to navigate complexities and seize opportunities. As Uganda charts its path toward inclusive growth, the lessons and foundations of 2024 will serve as a compass for shaping a sustainable and prosperous future.
The post Uganda’s economy exhibited resilience amidst global challenges in 2024 appeared first on The Independent Uganda:.
















